onDataSetupCompleteError()里面会对建立数据业务错误时,modem返回的retry时间进行判断,大概retry会分如下2种:
1.同一个apn的retry.
2.上一个apn retry 完后,进行下一个apn的retry.
下面只大概的讲下retry的逻辑,其他如怎么用alarmmanger进行设计retry的只是要注意定时和RTC的关系就可以了.
1.同一个apn的retry如下:
同一个APN Retry的最大次数是3次(MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY). 在建立Data Call的时候在方法setupData里面会通过方法apnSetting = apnContext.getNextApnSetting();再通过mRetryManager.getNextApnSetting()去判断modem层建议的retry时间(mModemSuggestedDelay)是否等于NO_SUGGESTED_RETRY_DELAY. 如果是第一次建立数据业务那么retry时间(mModemSuggestedDelay)肯定是不等于NO_SUGGESTED_RETRY_DELAY的,那么就会获得mWaitingApns里面的apn. 如果是在建立数据业务后的重试,那么如果if (mModemSuggestedDelay != NO_SUGGESTED_RETRY_DELAY &&
mSameApnRetryCount < MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY) 成立就会继续使用当前的apn进行建立,而不是去取mWaitingApns里面的下一个apn.
关键性的代码如下:
private static final int MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY = 3;
下面是建立失败后对是否要retry进行判断,如果要retry就返回Retry的时间.
public long getDelayForNextApn(boolean failFastEnabled) {
if (mWaitingApns == null || mWaitingApns.size() == 0) {
log("Waiting APN list is null or empty.");
return NO_RETRY;
}
if (mModemSuggestedDelay == NO_RETRY) {
log("Modem suggested not retrying.");
return NO_RETRY;
}
if (mModemSuggestedDelay != NO_SUGGESTED_RETRY_DELAY &&
mSameApnRetryCount < MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY) {
// If the modem explicitly suggests a retry delay, we should use it, even in fail fast
// mode.
log("Modem suggested retry in " + mModemSuggestedDelay + " ms.");
return mModemSuggestedDelay;
}
................................................
}
在上面判断需要Retry后,会通过AlarmManger进行定时进行同一个APN的Retry动作,关键代码如下:
通过setupData()方法调用apnContext.getNextApnSetting(),再调用mRetryManager.getNextApnSetting()方法,获得的还是上次失败的APN. 通过mCurrentApnIndex来控制mWaitingApns返回的是哪个APN.
public ApnSetting getNextApnSetting() {
if (mWaitingApns == null || mWaitingApns.size() == 0) {
log("Waiting APN list is null or empty.");
return null;
}
// If the modem had suggested a retry delay, we should retry the current APN again
// (up to MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY times) instead of getting the next APN setting from
// our own list.
if (mModemSuggestedDelay != NO_SUGGESTED_RETRY_DELAY &&
mSameApnRetryCount < MAX_SAME_APN_RETRY) {
mSameApnRetryCount++;
return mWaitingApns.get(mCurrentApnIndex);
}
....................................................................
}
2. 上一个APN已经Retry failed,那么就会从mWaitingApns里面的获得下一个将要Retry的APN.
如果数据业务建立失败了且失败的原因是permanent failure,那么就会设置该ApnSetting的permanentFailed的属性为True.
// If the data call failure cause is a permanent failure, we mark the APN as permanent
// failed.
if (isPermanentFail(cause)) {
log("cause = " + cause + ", mark apn as permanent failed. apn = " + apn);
apnContext.markApnPermanentFailed(apn);
}
最后会调到RetryManager里面的markApnPermanentFailed方法来设置对应的属性,
public void markApnPermanentFailed(ApnSetting apn) {
if (apn != null) {
apn.permanentFailed = true;
}
}
下面讲Retry逻辑,RetryManager类里面的getDelayForNextApn()完成是否要进行下一个APN Retry的判读,关键代码如下:
public long getDelayForNextApn\(boolean failFastEnabled\) {
..........................同一个APN的Retry逻辑..................................................
// In order to determine the delay to try next APN, we need to peek the next available APN.
// Case 1 - If we will start the next round of APN trying,
// we use the exponential-growth delay. \(e.g. 5s, 10s, 30s...etc.\)
// Case 2 - If we are still within the same round of APN trying,
// we use the fixed standard delay between APNs. \(e.g. 20s\)
....................................Block 1 start...................................................
int index = mCurrentApnIndex;
while (true) {
if (++index >= mWaitingApns.size()) index = 0;
// Stop if we find the non-failed APN.
if (mWaitingApns.get(index).permanentFailed == false) break;
// If we've already cycled through all the APNs, that means all APNs have
// permanently failed
if (index == mCurrentApnIndex) {
log("All APNs have permanently failed.");
return NO_RETRY;
}
}
....................................Block 1 end......................................................
....................................Block 2 start.............................................................
long delay;
if (index <= mCurrentApnIndex) {
// Case 1, if the next APN is in the next round.
if (!mRetryForever && mRetryCount + 1 > mMaxRetryCount) {
log("Reached maximum retry count " + mMaxRetryCount + ".");
return NO_RETRY;
}
delay = getRetryTimer();
++mRetryCount;
} else {
// Case 2, if the next APN is still in the same round.
delay = mInterApnDelay;
}
....................................Block2 end...............................................................
if (failFastEnabled && delay > mFailFastInterApnDelay) {
// If we enable fail fast mode, and the delay we got is longer than
// fail-fast delay (mFailFastInterApnDelay), use the fail-fast delay.
// If the delay we calculated is already shorter than fail-fast delay,
// then ignore fail-fast delay.
delay = mFailFastInterApnDelay;
}
return delay;
}
上面block1 代码块解释,index = mCurrentApnIndex,
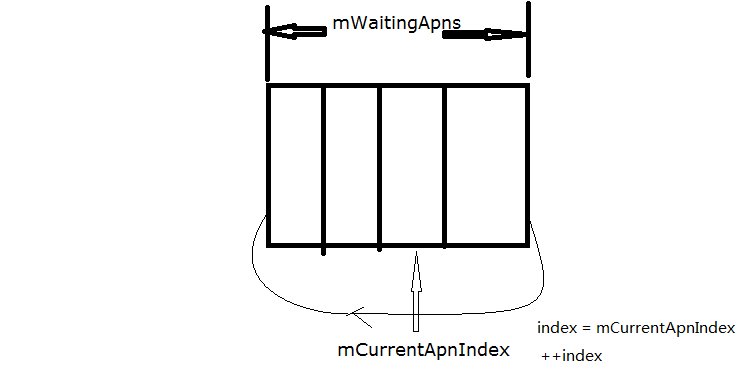
- 假如index++ < mWaitingApns的size,也就说当前建立失败的apn不是mWaitingApns的最后一个,那么用在前面加1后的index判读对应的apn是否为permanentFailed为true的apn,如果permanentFailed为false,就说明找到了可以用的apn了.
- 假如index++ < mWaitingApns的size,也就说当前建立失败的apn不是mWaitingApns的最后一个,那么用在前面加1后的index判读对应的apn是否为permanentFailed为true的apn,如果permanentFailed为true,那么就会继续的对index做加1的操作并判读对应的apn的peramanent 为ture,如果后面的apn在index+1的情况下对应的peramanent都为true,当循环一圈后(index == mCurrentApnIndex)就表明所有的apn都建立数据业务失败,就说明整个建立数据业务失败了.
上面代码块2解释,
在上面1的情况下,就说明还有apn可以用于数据业务的建立,
1.在trySetupData()的时候,会通过buildWaitingApns()方法去创建waitingApns,并调用apnContext.setWaitingApns(waitingApns)方法最终调用configureRetry来设置个waiting apn支持retry的时间隔.
2.if (index <= mCurrentApnIndex),暂时没有理解到源码为什么要=符号做为判断条件,我的理解走到这里,已经说明mCurrentApnIndex对应的apn重试次数完成了(block1代码块已经说明了index == mCurrentApnIndex为no retry).所以我觉得这里是个不严谨的代码.这里只说index < mCurrentApnIndex的情况,说明已经找到了新的apn作为数据业务的建立.这里就是不同apn的重试时间间隔了.通过下面的方法完成getRetryTimer();根据mRetryCount(retry时间间隔数组中的index)来取得对应apn的retry时间。